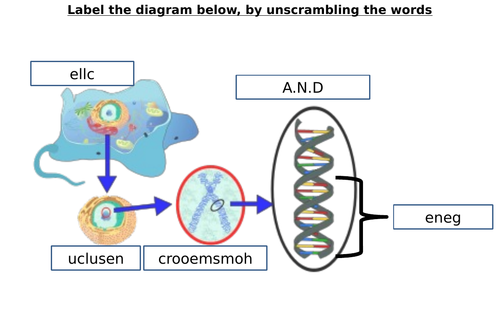
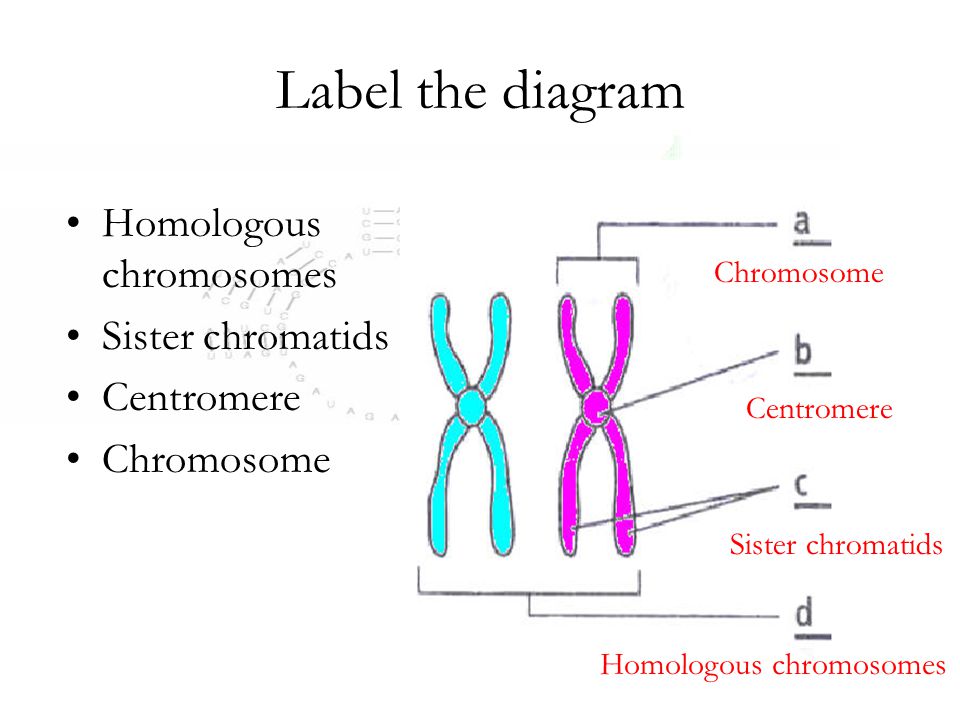
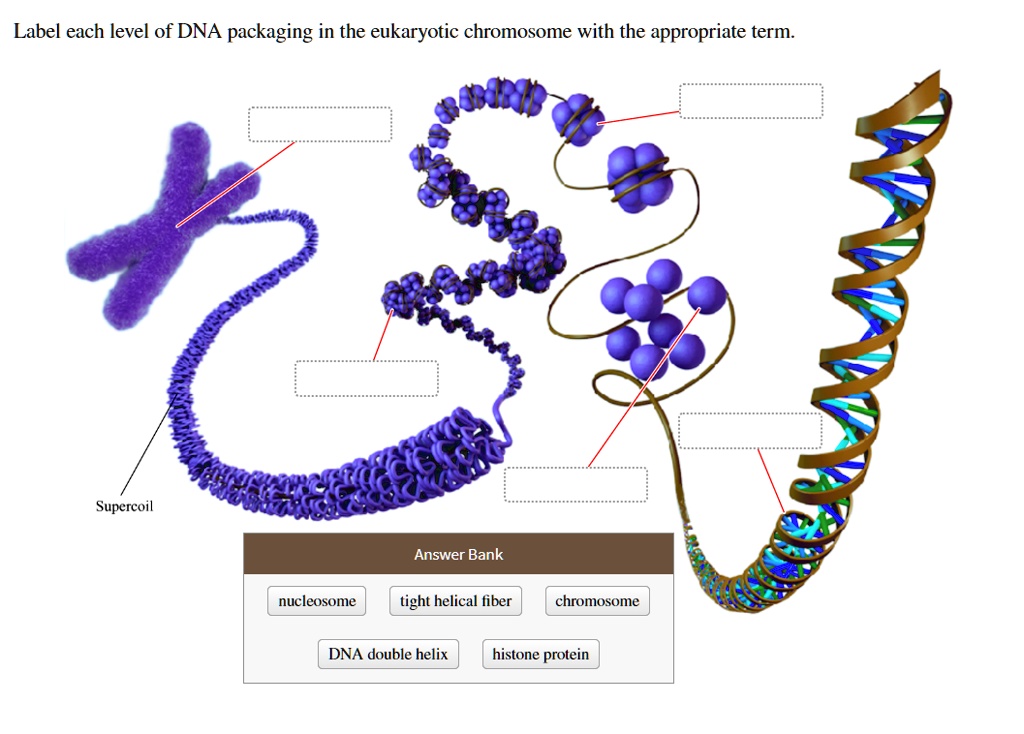
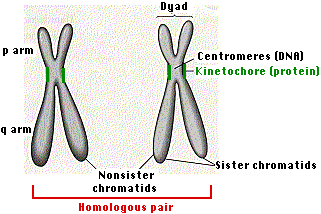
40 label the chromosome
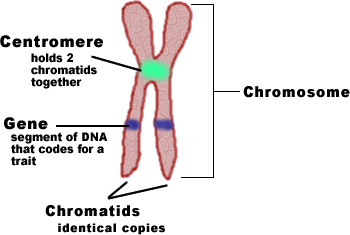
10.1C: Eukaryotic Chromosomal Structure and Compaction Eukaryotic Chromosomal Structure and Compaction. If the DNA from all 46 chromosomes in a human cell nucleus was laid out end to end, it would measure approximately two meters. However, the diameter would be only 2 nm. Considering that the size of a typical human cell is about 10 µm (100,000 cells lined up to equal one meter), DNA must be ... Chromatid - Genome.gov The two "sister" chromatids are joined at a constricted region of the chromosome called the centromere. During cell division, spindle fibers attach to the centromere and pull each of the sister chromatids to opposite sides of the cell. Soon after, the cell divides in two, resulting in daughter cells with identical DNA. Narration 00:00 … Chromatid.
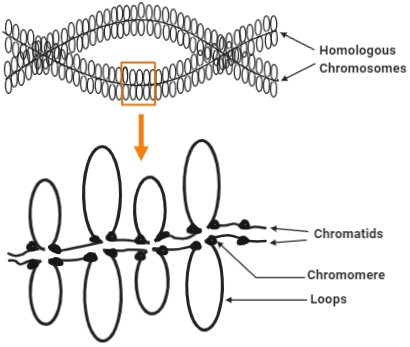
6 Main Parts of a Chromosome - Biology Discussion The following points highlight the six main parts of a chromosome. The parts are: 1. Pellicle and Matrix 2. Chromatids, Chromonema and Chromomeres 3. Centromeres 4. Secondary Constriction 5. Satellite 6. Telomere. Part # 1. Pellicle and Matrix: A membrane which surrounds each chromosome is said as pellicle.

Label the chromosome
Solved Indicate the heterochromatic and euchromatic regions - Chegg Expert Answer. 100% (7 ratings) Transcribed image text: Indicate the heterochromatic and euchromatic regions of the chromosome, and label the chromosome's centromeric and telomeric regions. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. The Stages of Mitosis and Cell Division - ThoughtCo The paired centromeres in each distinct chromosome begin to move apart. Once the paired sister chromatids separate from one another, each is considered a "full" chromosome. They are referred to as daughter chromosomes. Through the spindle apparatus, the daughter chromosomes move to the poles at opposite ends of the cell. Mitosis (Definition, Diagram & Stages Of Mitosis) - BYJUS The stages of Mitosis are: Prophase - The chromosomes shorten and thicken. Metaphase - Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. Anaphase - Chromatids break apart at the centromere and move to opposite poles. Telophase - Two nuclei formed after nuclear envelopes reform around each group of chromosomes.
Label the chromosome. What is a chromosome?: MedlinePlus Genetics Chromosomes are not visible in the cell’s nucleus—not even under a microscope—when the cell is not dividing. However, the DNA that makes up chromosomes becomes more tightly packed during cell division and is then visible under a microscope. Most of what researchers know about chromosomes was learned by observing chromosomes during cell division. Each chromosome has a constriction point called the centromere, which divides the chromosome into two sections, or “arms.”. How do geneticists indicate the location of a gene? - MedlinePlus The sex chromosomes are designated by X or Y. The arm of the chromosome. Each chromosome is divided into two sections (arms) based on the location of a narrowing (constriction) called the centromere. By convention, the shorter arm is called p, and the longer arm is called q. The chromosome arm is the second part of the gene's address. Chromosome Banding and Nomenclature - National Center for Biotechnology ... Each human chromosome has a short arm ("p" for "petit") and long arm ("q" for "queue"), separated by a centromere.The ends of the chromosome are called telomeres.. Each chromosome arm is divided into regions, or cytogenetic bands, that can be seen using a microscope and special stains.The cytogenetic bands are labeled p1, p2, p3, q1, q2, q3, etc., counting from the centromere out toward the ... Chromosome Map - Genes and Disease - NCBI Bookshelf Chromosome 1 is the largest and is over three times bigger than chromosome 22. The 23rd pair of chromosomes are two special chromosomes, X and Y, that determine our sex. Females have a pair of X chromosomes (46, XX), whereas males have one X and one Y chromosomes (46, XY). Chromosomes are made of DNA, and genes are special units of chromosomal DNA.
Lab 3 - Mitosis and Meiosis- eScience Labs - StuDocu Identify how this chromosome appears physically different on a karyotype than it appears on a karyotype of normal chromosomes. a. The Philadelphia chromosome is when a piece of chromosome 9 and a piece of chromosome 22 break apart and trade places, the change was coined the Philadelphia chromosomes where the piece of chromosome 9 forms onto ... Labeling of Chromosomes in Cell Development and ... - Hindawi As an example, we can label a pair of homologous chromosomes in the initial state of the zygote at the root of the tree as [(AB), (ab)]. Consequently, the cell labeling associated with the two possible combinations after the first division can be represented by Figure 4 from Berkovich and Bloom . The states of the internal cellular clock are ... Top Labeled Chromosome Images, Diagrams and Structure (Download) Labeled chromosome structure and diagrams show that chromosomes are made up of arms joined by the centromere and have genes on them. Chromosomes are important for our life as total DNA is located on 23 pairs of human chromosomes. Any sudden or long-term alteration causes serious problems for a person. ch 8 mastering biology Flashcards | Quizlet Drag the pink labels onto the pink targets to identify the two main phases of the cell cycle. Then drag the blue labels onto the blue targets to identify the key stages that occur during those phases. a g1 phase b. s phase c. interphase d. g2 phase e. mitotic m phase f. mitosis g. cytokinesis Activity: The Cell Cycle Part A Part complete
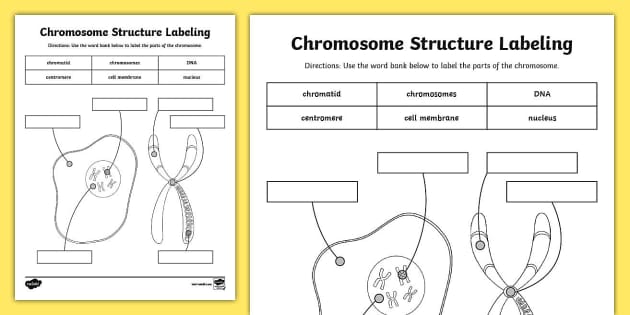
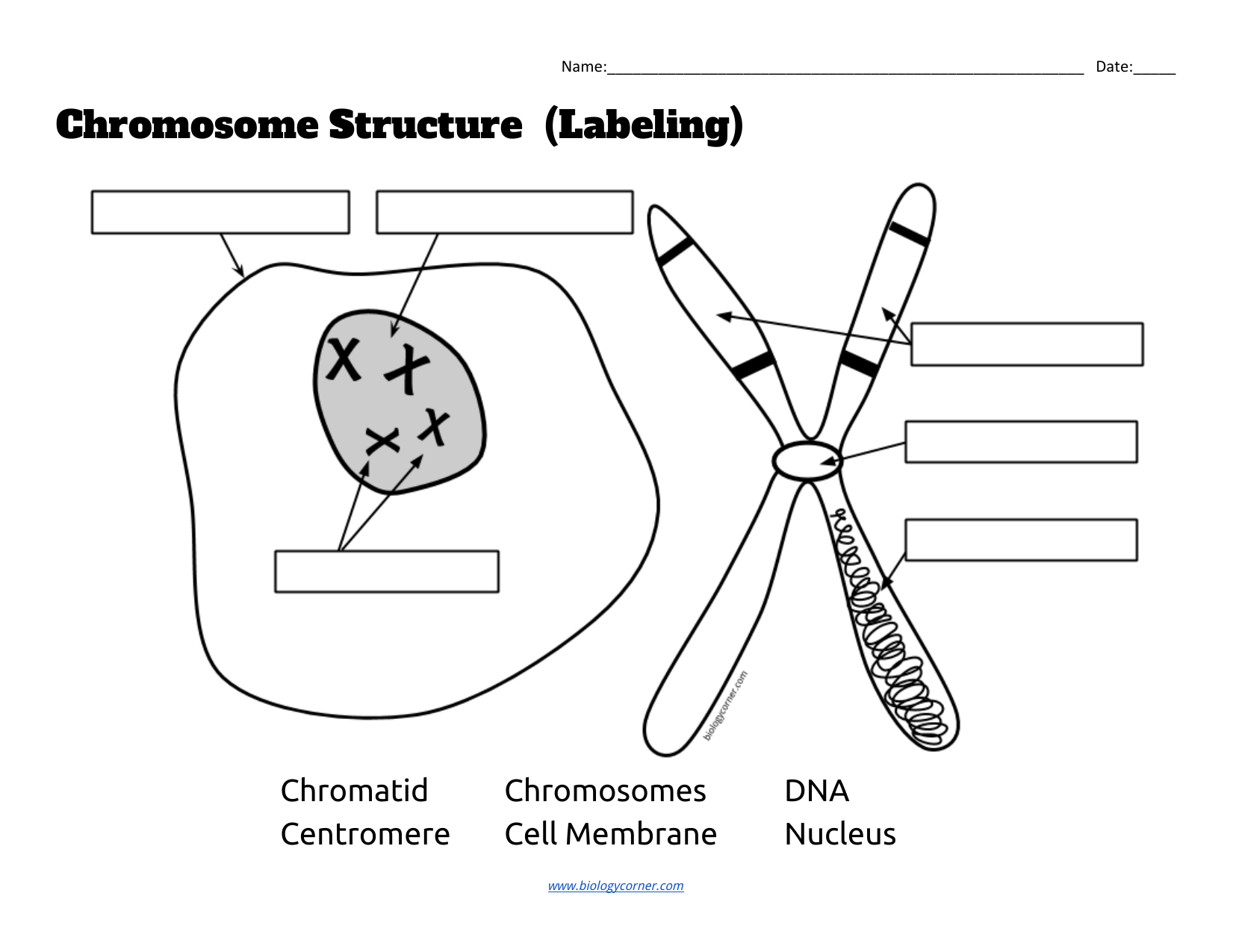
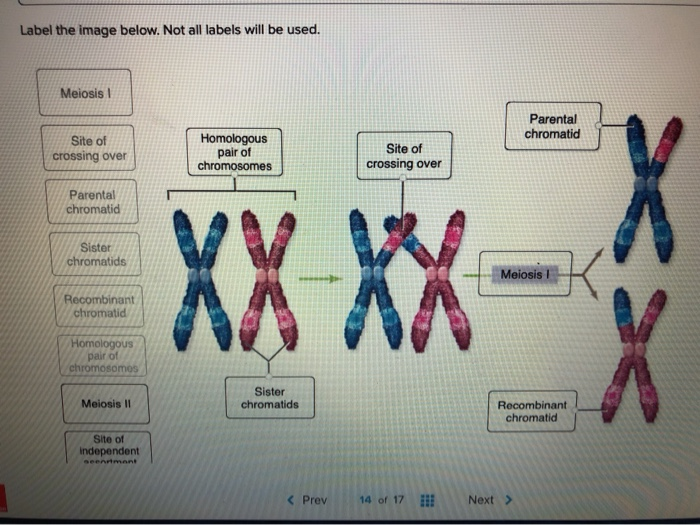
Chromosome Structure Labeling - The Biology Corner Students label a simple diagram of a chromosome showing the centromere, chromatid, DNA, and the location of the chromosome within the nucleus of a cell. Name:_____Date: _____ Chromosome Structure (Labeling) Chromatid Chromosomes DNA Centromere Cell_Membrane Nucleus This work is licensed under a ... Chromosome - Definition, Function & Structure | Biology Dictionary Chromosome Definition A chromosome is a string of DNA wrapped around associated proteins that give the connected nucleic acid bases a structure. During interphase of the cell cycle, the chromosome exists in a loose structure, so proteins can be translated from the DNA and the DNA can be replicated. Answered: 3. Draw and label the chromosome at… | bartleby Draw and label the chromosome at Anaphase I. Anaphase I Chromosome number per pole Right pole: 2 chromosomes Left pole: 2 chromosomes Chromosome composition per pole ** Right pole: 1 long chromosome (la) and short chromosome (2c) Left pole: 1 long chromosome (1b) and 1 short chromosome (2d) 3.a How is the Anaphase I differ from Anaphase? A Labelled Diagram Of Meiosis with Detailed Explanation - BYJUS Here, the chromosomes begin to condense. Prophase I is divided into five different stages: Leptotene Zygotene Pachytene Diplotene Diakinesis Metaphase I The homologous pairs of chromosomes are aligned on the equatorial plate. Anaphase I The homologous chromosomes are pulled on the opposite poles. The sister chromatids remain attached to each other.
Draw the structure of the chromosome and label its parts. 10 Jan 2023 — Centromere – Centromere is a specialized DNA sequence of a chromosome which links a pair of sister chromatids. During mitosis or meiosis the ...
Chromosome Structure (Labeling) - The Biology Corner Jun 3, 2019 · Chromosome Structure. This simple worksheet shows a diagram of a chromosome and where it is located in the nucleus of the cell. Students use a word bank to label the chromatid, centromere, chromosomes, cell membrane, DNA, and nucleus. This worksheet was created for introductory biology for students to practice labeling the parts of a chromosome.
Chromosome | Structure & Function | Britannica chromosome, the microscopic threadlike part of the cell that carries hereditary information in the form of genes. A defining feature of any chromosome is its compactness. For instance, the 46 chromosomes found in human cells have a combined length of 200 nm (1 nm = 10− 9 metre); if the chromosomes were to be unraveled, the genetic material they contain would measure roughly 2 metres (about 6 ...
Chromosomes (article) | Khan Academy Chromosomes Chromosomes, chromatids and chromatin Chromosome structure and numbers review Chromosomes Science> High school biology> Reproduction and cell division> Chromosome structure and numbers © 2023 Khan Academy Terms of usePrivacy PolicyCookie Notice Chromosomes Google Classroom Loading...
4 Types of Chromosome Mutations -Evolution and Genetics - ThoughtCo Deletion. Crossing Over. Getty/FRANCIS LEROY, BIOCOSMOS. If a mistake is made during meiosis that causes part of a chromosome to break off and become lost, this is called a deletion. If the deletion occurs within a gene that is vital for the survival of an individual, it could cause serious problems and even death for a zygote made from that ...
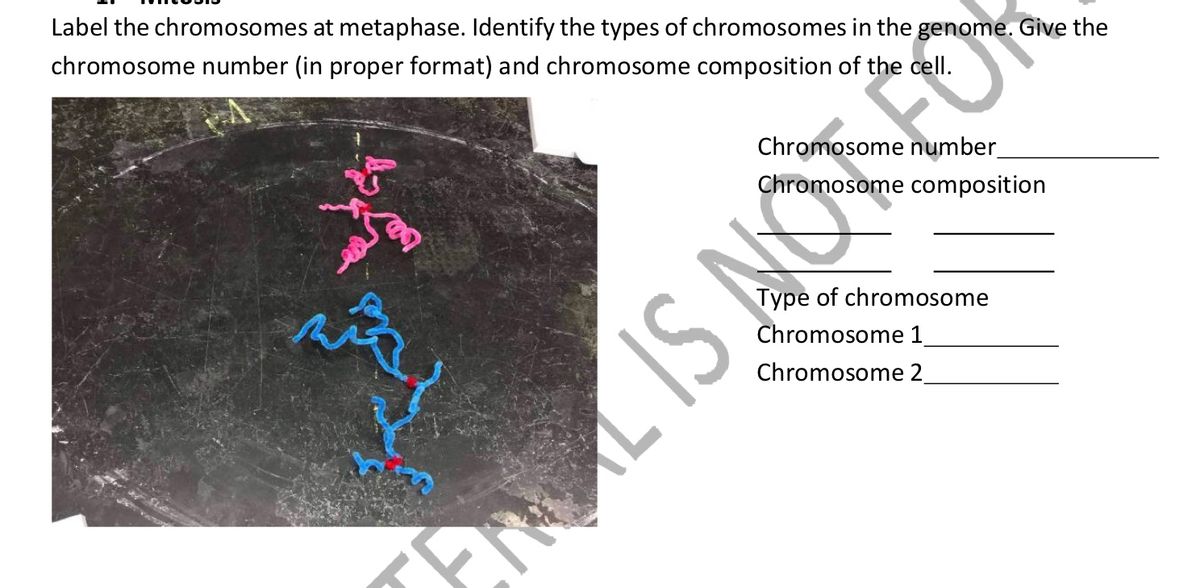
Answered: 2. Draw and label the chromosomes at… | bartleby Draw and label the chromosomes at metaphase I Metaphase I Chromosome number: Right pole: 2 chromosomes Left pole: 2 chromosomes Chromosome composition: 1 pair of bivalent short chromosome and 1 pair of bivalent long chromosome Question thumb_up 100% Please help me explain this thank you Transcribed Image Text: 2.
The 4 Mitosis Phases: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase Once the chromatin has condensed into individual chromosomes, the genetically-identical chromosomes come together to form an "X" shape, called sister chromatids. These sister chromatids carry identical DNA and are joined at the center (in the middle of the "X" shape) at a point called the centromere.
Lab Manual Exercise #2 - Palomar College Three blue chromosomes (a, b & c) in this cell represent one haploid set of paternal chromosomes from the father. Since there are 2 sets of chromosomes in this diagram, the cell is diploid (2n). One chromatid of this eukaryotic chromosome doublet is unravelled, showing a twisted DNA molecule wrapped around beads of histone protein. Each protein ...
DNA, Genes & Chromosomes Overview - Cleveland Clinic Chromosomes are structures that look like thread, which live in the nucleus (center) of cells. One molecule of DNA and one protein make up one chromosome. Chromosomes are different sizes, and proteins called histones allow them to pack up small enough to fit in a nucleus. Without these, our chromosomes would be as tall as we are!
Chromosomes Fact Sheet - Genome.gov Aug 15, 2020 · Chromosomes are thread-like structures located inside the nucleus of animal and plant cells. Each chromosome is made of protein and a single molecule of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Passed from parents to offspring, DNA contains the specific instructions that make each type of living creature unique. The term chromosome comes from the Greek words for color (chroma) and body (soma).
Chromosome: its Parts, Functions and Types (1934 Words) | Biology Each chromosome is bounded by a membrane called pellicle. It is very thin and is formed of achromatic substance. This membrane encloses a jelly-like substance which is usually called matrix. In the matrix is present the chromonemata. The matrix is also formed of achromatic or nongenic material.
Label the Chromosome Diagram | Quizlet Label the Chromosome 3.0 (2 reviews) + − Flashcards Learn Test Match Created by casey_cummings2 Terms in this set (5) Chromosome ... Centromere ... Chromatid ... Chromatid ... Chromosome A __________ Carries Genetic Information Sets found in the same folder Mitosis 22 terms Nicole694 DNA structure 20 terms muskopf1 STAAR Biology Category #1
Mitosis (Definition, Diagram & Stages Of Mitosis) - BYJUS The stages of Mitosis are: Prophase - The chromosomes shorten and thicken. Metaphase - Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. Anaphase - Chromatids break apart at the centromere and move to opposite poles. Telophase - Two nuclei formed after nuclear envelopes reform around each group of chromosomes.
The Stages of Mitosis and Cell Division - ThoughtCo The paired centromeres in each distinct chromosome begin to move apart. Once the paired sister chromatids separate from one another, each is considered a "full" chromosome. They are referred to as daughter chromosomes. Through the spindle apparatus, the daughter chromosomes move to the poles at opposite ends of the cell.
Solved Indicate the heterochromatic and euchromatic regions - Chegg Expert Answer. 100% (7 ratings) Transcribed image text: Indicate the heterochromatic and euchromatic regions of the chromosome, and label the chromosome's centromeric and telomeric regions. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets.




























Komentar
Posting Komentar